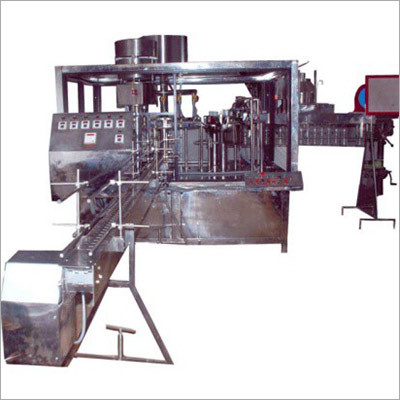
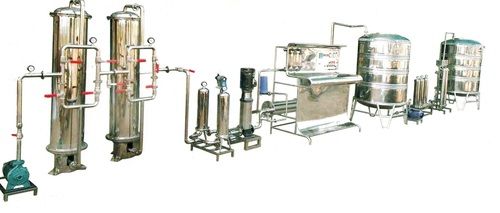
Water Treatment Plant
Product Details:
- Product Type Water Treatment Plant
- Click to View more
Water Treatment Plant Product Specifications
- Water Treatment Plant
Water Treatment Plant Trade Information
- Asia Australia Central America North America South America Eastern Europe Western Europe Middle East Africa
- All India
Product Description
The term "water treatment plant" refers to a facility that processes and treats wastewater to eliminate impurities and pollutants before releasing the purified water back into the environment or recycling it for other uses. A water treatment facility's main objective is to guarantee that the water it produces satisfies strict quality requirements for safe disposal or reuse.
The general steps in the water treatment procedure at a typical water treatment facility are as follows:
1. Raw wastewater is gathered from residential, commercial, and industrial sources using a system of underground pipelines or sewage systems, then it is screened. Through screens and bar racks, large debris and solid objects like rocks, sticks and rubbish are removed.
2. Primary Treatment: During primary treatment, suspended particles and organic debris are taken out of the wastewater. Physical procedures like flotation and sedimentation are used to accomplish this. Lighter materials float to the surface for evacuation whereas heavier elements sink in the presence of gravity and produce sludge at the bottom.
3. Secondary Treatment: The partially treated wastewater then moves on to the biological, or secondary, treatment, step. In this stage, bacteria and fungi among other microbes decompose and consume organic debris, further decreasing pollution. The activated sludge process, in which wastewater is combined with a "seed sludge" containing the microorganisms, is the most used secondary treatment technique.
4. Tertiary Treatment: Some water treatment facilities additionally have this stage of advanced treatment, which is intended to get rid of any last-resort impurities and raise the standard of the water even higher. Additional filtration, disinfection, or chemical processes may be used at this stage to remove particular pollutants, such as trace metals, nitrogen and phosphorus compounds, or other pollutants.
5. After primary and secondary treatment, the water is disinfected to get rid of any germs that could cause illness. Chlorination, UV light, and ozonation are common disinfection techniques. The disinfection procedure makes sure that the cleaned water is secure enough to be reused or released into the environment.
6. Sludge Treatment: Solid waste, or sludge, is produced throughout the treatment process. The solids and biomass that were collected during the primary and secondary treatment steps are included in this sludge. Sludge undergoes separate treatment to reduce volume and eliminate water content. The resulting sludge can then be handled for safe disposal (using anaerobic digestion, for example) or used for things like land application or energy production.
7. Effluent Discharge or Water Reuse: The treated water, often referred to as effluent, is normally discharged in accordance with legal requirements and environmental standards into rivers, lakes, or oceans. Sometimes, the treated water is subjected to further purification in order to be used for a particular reuse, such as irrigation, industrial activities, or groundwater recharge.
It's vital to remember that the specific procedures and tools employed in a water treatment facility can change based on elements like the size of the building, the standard of the entering sewage, and the intended use of the treated water. There may be particular laws and rules controlling water treatment practises in various states, provinces, and nations.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Mineral Water Processing Plant' category
 |
ACCURAL BIOTECH
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |